Sepsis - spotting the signs
Fever is extremely common in children and usually suggests that your child has an infection. A child has a fever if their temperature is 38.0°C (100.4°F) or above. The most accurate way of measuring your child’s temperature is with a digital thermometer.
- Viral infections are far more common than bacterial infections.
- Symptoms such as runny nose, cough, wheeze, sore throat, red eyes and diarrhoea are more suggestive of a viral infection than a bacterial infection. If a number of people are unwell in the same household, this also suggests a viral infection (because viral infections are easily spread). Viral infections do not treatment with antibiotics.
- Sepsis is a rare but serious form of bacterial infection which needs to be diagnosed and treated early.
- The diagnosis of sepsis is initially based on simple measurements such as temperature, heart rate and breathing rate.
- For further information on sepsis, click here
When should you worry?
If your child has any of the following:
- Becomes pale, mottled and feels abnormally cold to touch
- Is going blue around the lips
- Too breathless to talk / eat or drink
- Has a fit/ seizure
- Becomes extremely agitated (crying inconsolably despite distraction), confused or very lethargic (difficult to wake)
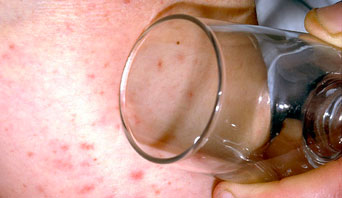
- Develops a rash that does not disappear with pressure (the ‘Glass Test’)
- Is under 1 month of age with a temperature of 38°C / 100.4°F or above
You need urgent help.
Go to the nearest Hospital Emergency (A&E) Department or phone 999
If your child has any of the following:
- Is finding it hard to breathe
- Seems dehydrated (sunken eyes, drowsy or not passed urine for 12 hours)
- Is becoming drowsy (excessively sleepy) or irritable (unable to settle them with toys, TV, food or picking up) – especially if they remain drowsy or irritable despite their fever coming down
- Has extreme shivering or complains of muscle pain
- Is 1-3 months of age with a temperature of 38°C / 100.4°F or above, or 3-6 months of age with a temperature of 39°C / 102.2°F or above (but fever is common in babies up to 2 days after they receive vaccinations)
- Continues to have a fever of 38.0°C or above for more than 5 days
- Is getting worse or if you are worried
You need to contact a doctor or nurse today.
Please ring your GP surgery or call NHS 111 - dial 111
We recognise that during the current COVID-19 crisis, at peak times, access to a health care professional may be delayed. If symptoms persist for 4 hours or more and you have not been able to speak to either a member of staff from your GP practice or to NHS 111 staff, then consider taking them to your nearest ED.
If none of the above features are present
Additional advice is also available to young families for coping with crying of well babies – click here.
Self care
Continue providing your child’s care at home. If you are still concerned about your child, call NHS 111 – dial 111
What should you do if your child has a fever but no signs of sepsis?
- To make your child more comfortable, you may want to lower their temperature using paracetamol (calpol) and/or ibuprofen. However, remember that fever is a normal response that may help the body to fight infection and paracetamol/ibuprofen will not get rid of it entirely.
- Avoid tepid sponging your child – it doesn’t actually reduce your child’s temperature and may cause your child to shiver.
- Encourage them to drink plenty of fluids.
- If a rash appears, do the glass test.
How long will it take for my child to get better?
- Fever caused by a viral infection tends to improve within 2 to 3 days.
- If your child’s fever lasts for more than 5 days and they are not getting any better in themselves, get them seen by your GP.
- The chart below shows how long fever lasts in a child with viral infections. The faces represent 10 children who have seen their GP with a viral infection. Green faces are those children whose fever has recovered within that time period.

The diagram is taken from 'When should I worry'
Where should you seek help?
- If it is non-urgent, speak to your local pharmacist or health visitor.
- If your child has any of the above features, urgently see your GP. For an urgent out-of-hours GP appointment, call NHS 111.
- You should only call 999 or go your nearest A&E department in critical or life threatening situations
For wear and tear, minor trips and everything in between.
Self-care
You can treat your child's very minor illnesses and injuries at home.
Some illnesses can be treated in your own home with support and advice from the services listed when required, using the recommended medicines and getting plenty of rest.
Sound advice
Children can recover from illness quickly but also can become more poorly quickly; it is important to seek further advice if a child's condition gets worse.
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
For wear and tear, minor trips and everything in between.
Self-care
You can treat your child's very minor illnesses and injuries at home.
Some illnesses can be treated in your own home with support and advice from the services listed when required, using the recommended medicines and getting plenty of rest.
Sound advice
Children can recover from illness quickly but also can become more poorly quickly; it is important to seek further advice if a child's condition gets worse.
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
Pharmacists are experts in many aspects of healthcare and can offer advice on a wide range of long-term conditions and common illnesses such as coughs, colds and stomach upsets. You don’t need an appointment and many have private consultation areas, so they are a good first port of call. Your pharmacist will say if you need further medical attention.
Sound advice
- Visit a pharmacy if your child is ill, but does not need to see a GP.
- Remember that if your child's condition gets worse, you should seek further medical advice immediately.
- Help your child to understand - watch this video with them about going to the pharmacy.
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
Pharmacists are experts in many aspects of healthcare and can offer advice on a wide range of long-term conditions and common illnesses such as coughs, colds and stomach upsets. You don’t need an appointment and many have private consultation areas, so they are a good first port of call. Your pharmacist will say if you need further medical attention.
Sound advice
- Visit a pharmacy if your child is ill, but does not need to see a GP.
- Remember that if your child's condition gets worse, you should seek further medical advice immediately.
- Help your child to understand - watch this video with them about going to the pharmacy.
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
Health visitors are nurses or midwives who are passionate about promoting healthy lifestyles and preventing illness through the delivery of the Healthy Child Programme. They work with you through your pregnancy up until your child is ready to start school.
Health Visitors can also make referrals for you to other health professionals for example hearing or vision concerns or to the Community Paediatricians or to the child and adolescent mental health services.
Contact them by phoning your Health Visitor Team or local Children’s Centre.
Sound advice
Health visitors also provide advice, support and guidance in caring for your child, including:
- Breastfeeding, weaning and healthy eating
- Exercise, hygiene and safety
- Your child’s growth and development
- Emotional health and wellbeing, including postnatal depression
- Safety in the home
- Stopping smoking
- Contraception and sexual health
- Sleep and behaviour management (including temper tantrums!)
- Toilet training
- Minor illnesses
For more information watch the video: What does a health visitor do?
Health visitors are nurses or midwives who are passionate about promoting healthy lifestyles and preventing illness through the delivery of the Healthy Child Programme. They work with you through your pregnancy up until your child is ready to start school.
Health Visitors can also make referrals for you to other health professionals for example hearing or vision concerns or to the Community Paediatricians or to the child and adolescent mental health services.
Contact them by phoning your Health Visitor Team or local Children’s Centre.
Sound advice
Health visitors also provide advice, support and guidance in caring for your child, including:
- Breastfeeding, weaning and healthy eating
- Exercise, hygiene and safety
- Your child’s growth and development
- Emotional health and wellbeing, including postnatal depression
- Safety in the home
- Stopping smoking
- Contraception and sexual health
- Sleep and behaviour management (including temper tantrums!)
- Toilet training
- Minor illnesses
For more information watch the video: What does a health visitor do?
School nurses care for children and young people, aged 5-19, and their families, to ensure their health needs are supported within their school and community. They work closely with education staff and other agencies to support parents, carers and the children and young people, with physical and/or emotional health needs.
Primary and secondary schools have an allocated school nurse – telephone your child’s school to ask for the contact details of your named school nurse.
There is also a specialist nurse who works with families who choose to educate their children at home.
Sound Advice
Before your child starts school your health visitor will meet with the school nursing team to transfer their care to the school nursing service. The school nursing team consists of a school nursing lead, specialist public health practitioners and school health staff nurses.
They all have a role in preventing disease and promoting health and wellbeing, by:-
- encouraging healthier lifestyles
- offering immunisations
- giving information, advice and support to children, young people and their families
- supporting children with complex health needs
Each member of the team has links with many other professionals who also work with children including community paediatricians, child and adolescent mental health teams, health visitors and speech and language therapists. The school health nursing service also forms part of the multi-agency services for children, young people and families where there are child protection or safeguarding issues.
School nurses care for children and young people, aged 5-19, and their families, to ensure their health needs are supported within their school and community. They work closely with education staff and other agencies to support parents, carers and the children and young people, with physical and/or emotional health needs.
Primary and secondary schools have an allocated school nurse – telephone your child’s school to ask for the contact details of your named school nurse.
There is also a specialist nurse who works with families who choose to educate their children at home.
Sound Advice
Before your child starts school your health visitor will meet with the school nursing team to transfer their care to the school nursing service. The school nursing team consists of a school nursing lead, specialist public health practitioners and school health staff nurses.
They all have a role in preventing disease and promoting health and wellbeing, by:-
- encouraging healthier lifestyles
- offering immunisations
- giving information, advice and support to children, young people and their families
- supporting children with complex health needs
Each member of the team has links with many other professionals who also work with children including community paediatricians, child and adolescent mental health teams, health visitors and speech and language therapists. The school health nursing service also forms part of the multi-agency services for children, young people and families where there are child protection or safeguarding issues.