Exomphalos (omphalocele)
What is it?
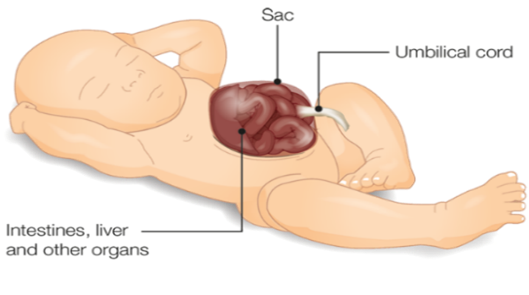
Exomphalos is an abdominal wall defect. With this condition some of the bowel or other abdominal organs protrude (poke out) through an opening where the umbilical cord is. This means that some of the organs may be lying in the umbilical cord.
A clear membrane covers the organs.
Why has this happened?
We do not know exactly what causes Exomphalos.
It is not caused by something you have or have not done. It is caused by an error in the development of the digestive tract.
Up to half of babies with Exomphalos have other birth defects or chromosomal
abnormalities.
Picture of baby with Exomphalos
What happens next?
Exomphalos may be seen at your first scan but in many cases is detected at the 20-week anomaly scan.
The scan findings will be discussed with you by the Fetal Medicine Midwife or appropriately trained professional.
You will be referred to the Fetal Medicine Clinic where you will see the Consultant Obstetrician for a further scan and more detailed discussion.
Pregnancy
Due to the high association of chromosomal abnormalities you will be offered the option of having a diagnostic test.
These are:
- CVS (Chorionic Villus Sampling)
This can be performed between 11 to 14 weeks of pregnancy. A small sample is removed from the placenta to test the cells (chromosomes). This is normally performed in Bristol Fetal Medicine Unit, St Michaels Hospital.
- Amniocentesis
This can be performed from 15 weeks onwards at the Royal Gwent Hospital. During this procedure, a sample of amniotic fluid is taken to test the cells (chromosomes)
For further information on both tests see ASW Website (Antenatal Screening Wales)
You will be offered a Fetal Echo at around 20 weeks of pregnancy to check baby’s heart and the vessels surrounding it.
You will be seen in Fetal Medicine Clinic for regular scans to assess baby’s wellbeing, how baby is growing and the amount of amniotic fluid present.
A referral will be sent to the Fetal Medicine Unit, University Hospital of Wales in Cardiff where you will be given an appointment to discuss further the condition and delivery.
Delivery
After giving birth your baby will need specialist care and an operation.
Cardiff is the closest Paediatric Surgical Unit and therefore the safest place for delivery.
Ideally the baby will be born by vaginal delivery, but Caesarean Section may be necessary if the Exomphalos is large. Options can be discussed later in pregnancy with the Fetal Medicine Consultant.
Further information regarding baby’s operation and after care will be given and you will have the opportunity to meet the surgeon and neonatal team before delivery.
Each baby’s outlook will depend on individual circumstances.
Support
We realise that it must be a difficult and stressful time for you. Please contact the Fetal Medicine Midwife on the number below if you have any further questions or concerns:
Contact Numbers
Royal Gwent Hospital 01633 234747
Nevill Hall Hospital 01873 732390 or 01873 732391
Cardiff Fetal Medicine Unit 02920 742279
Useful Websites
ARC (Antenatal Results and Choices) - Offer information and support to parents who are making decisions before, during and after tests in pregnancy
Tel no: 084507722990
Website: https://www.arc-uk.org/
Email: info@arc-uk-org
ASW (Antenatal Screening Wales)
Website: https://phw.nhs.wales/services-and-teams/screening/antenatal-screening-wales/
GEEPS :(information on Exomphalos and parent support)
Website: https://www.geeps.org/